Spanning Tree Hp Procurve
If you have a strong Cisco background, then you immediately think of Spanning Tree Protocol when you think of Layer 2 loop protection. Or if you’re keeping abreast of the newest developments, you think of TRILL and SPB. But there are other mechanisms for helping detect loops at layer 2. Here’s one I came across while studying for HP Master ASE: HP Procurve Loop-Protection.
- Spanning Tree Portfast Hp Switch
- Spanning Tree Portfast Hp Procurve
- Spanning Tree Priority Hp Procurve
- Hp Procurve Switch Firmware
According to the documentation:
Loop protection provides protection against loops by transmitting loop protocol packets out of ports on which loop protection has been enabled. When the switch sends out a loop protocol packet and then receives the same packet on a port that has a receiver-action of send-disable configured, it shuts down the port from which the packet was sent.
Invest in networking switches. HPE network switches are built to handle today’s network traffic as well as the inevitable future increase in traffic. They are agile, scalable, and secure and can be easily integrated into your existing Aruba infrastructure.
So it’s not doing anything fancy - just using its own protocol packet to detect loops back to the switch itself. Note this is different to Cisco’s loopback detection, which will detect a switchport looped back on itself - e.g. due to faulty wiring - but will not detect a cable run from one port to another on the same switch. Configuration is quick and easy, and it seems to work well. It should work well in any situation where you have edge ports that users might connect together, possibly via a ‘dumb’ switch that doesn’t forward STP BPDUs. These loop protection frames should be forwarded.
Let’s take a quick look at the configuration and operation on my lab switch, an HP 2910al-24G Procurve switch, running W.15.08.0012. The default configuration is for loop-protection to be disabled:
The HP ProCurve Switch 6200yl-24G-mGBIC is an advanced Layer 3 stackable switch in 1U height. It has 24 mini-GBIC slots and an expansion slot for an optional 4-port 10-GbE module. Designed to be deployed as an aggregator of traffic from the edge to. The ProCurve 5406zl Switch supplied Power over Ethernet (PoE) power for the Avaya IP telephones and was configured to support link aggregation, rapid spanning tree, load balancing, VLANs, enforce QoS policies, LLDP, and OSPF with the peer ProCurve switches. To Configure the Cisco 3750 to use MST(Multiple Spanning Tree) use the following commands: spanning-tree mode mst spanning-tree mst configuration name MYMST revision 10 instance 0 vlan 1-4094! On the Procurve side use this configuration: spanning-tree mode mst name MY-MST revision 10 instance 0 vlan 1-4094.
In my lab, I’ve run a cable between ports 21 and 22, so we can simulate a loop. Currently both ports are shut down. Spanning-tree is disabled on this switch, so if I enable those ports, we’ve got a loop, and things will get messy. Let’s configure loop protection, and then enable the ports:
OK, let’s take a look at what’s happened with our ports:
Pretty simple hey? One of the ports has been shut down, as expected. It has been logged, and an SNMP trap (OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.11.2.14.11.5.1.12.1.5.6.1) has been generated. We’ve got the “Port Disable Timer” at the default of “Disabled” - this means that the port will stay shut down until we take manual action. We’d like it to re-enable after 10s, so we configure this:
Now if we keep an eye on the output of show loop-protect we can see the Loop Count incrementing, as the port gets re-enabled, detects a loop, and shuts down again:
So now you can set a disable timer, and once users remove the loop, their network ports will come back up, without needing any input from the local network admin. All up, this is an easy feature to configure, and should be used on all edge ports on Procurve switches.
Comware has a very similar feature, called loopback-detection. Currently I don’t have any Comware-based devices in my lab though…unless someone wants to donate some?
5/5 (2)In this article we are going to explain what is the MSTP (Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol) procotolo, what are its benefits and how it is configured in HP switches.
What is the MSTP?
The MSTP protocol is an evolution of STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) used to prevent loops in networks where we want to give redundancy through a ring configuration. For those of you who do not know what STP is, you can consult the following link:this article.
Using the MSTP, we were able to improve the utilization of all links in the network. Basically it consists of blocking different links for VLAN groups.
Benefits of using MSTP
The main advantages of using MSTP are the following:
- Load balancing
- És a standardized protocol
- Minimize CPU usage compared to other STP protocols such as PVST.
- Compatible with other STP protocols.
Below is a graph with the diagram of a final MSTP configuration.
In this example, we see how the traffic of the 100-199 vlans will be blocked in one direction, while the vlans of the 200-299 will be allowed to pass through the blocked path. This improves network performance, since using STP or RSTP, one of these links would never be used.Design of the MSTP: Regions
An MST region is one that shares the spanning-tree configuration.
The switches will be in the same region if you have the maximum:
- Name of region
- Revision number
- Mapping of VLAN-to-instance
Bb king live at the regal flac. So if we want to have several switches in the same region, what we will do is configure these same parameters in all the switches.
How to configure MSTP in HP switches?
Steps to configure the MSTP in an HP-2530 switch:
- Configure the VLANS
Configure the VLANS
- Define the MST
region
Spanning Tree Portfast Hp Switch
- Define the revision number in the MST region
- Define VLAN-to-instance mapping.
- Define the priority for each
- Define the cost of the path (path-cost)
- Define point-to-point links
- Enable MSTP
Example: Configure MSTP on switch HP 2530
We will take as an example the same scheme as in the aforementioned article.
In this case all switches are HP2530 model.
Design conditions:
Switch A: Root for vlans 100-199
Switch B: Root for vlans 200-299
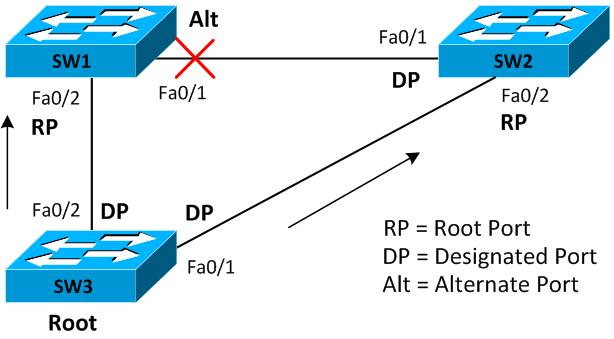
Switch C: You will have the ports blocked for each instance.
Spanning Tree Portfast Hp Procurve
Switch A configuration:
Spanning Tree Priority Hp Procurve
mstp name mstp-example
mstp revision 10 mstp revision 10
mstp instance 1 vlan 100 to 199
mstp instance 1 priority 0
mstp instance 2 vlan 200 to 299
mstp instance 2 priority 4096
mstp instance 2 ethe 3/3 path-cost 30000
mstp admin-pt2pt-mac ethe 3/1 to 3/3
mstp start
Switch B configuration:
Hp Procurve Switch Firmware
mstp name mstp-example
mstp revision 10 mstp revision 10
mstp instance 1 vlan 100 to 199
mstp instance 1 priority 4096
mstp instance 2 vlan 200 to 299
mstp instance 2 priority 0
mstp instance 2 ethe 3/3 path-cost 30000
mstp admin-pt2pt-mac ethe 3/1 to 3/3
mstp start
Swtich C configuration:
mstp name mstp-example
mstp revision 10
mstp instance 1 vlan 100 to 199
mstp instance 2 vlan 200 to 299
mstp start
With these commands and bearing in mind that the cables are connected correctly, we will have our equipment configured correctly.
If you have any questions, do not hesitate to comment or send me your questions.
See you in the nets!
